Others also read
| Visual distortion in architectural glazing has emerged as a critical yet insufficiently regulated factor affecting both functional performance and visual comfort.
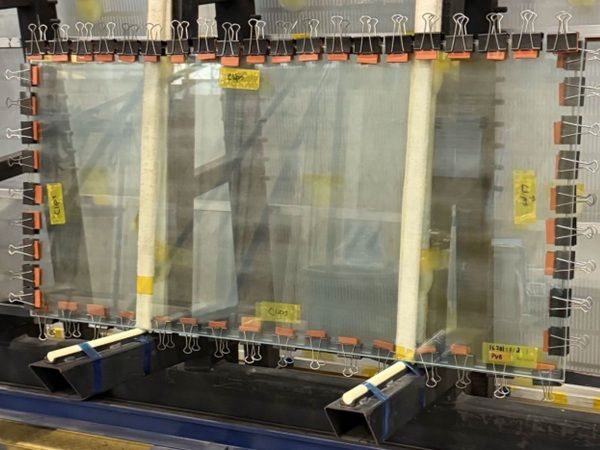
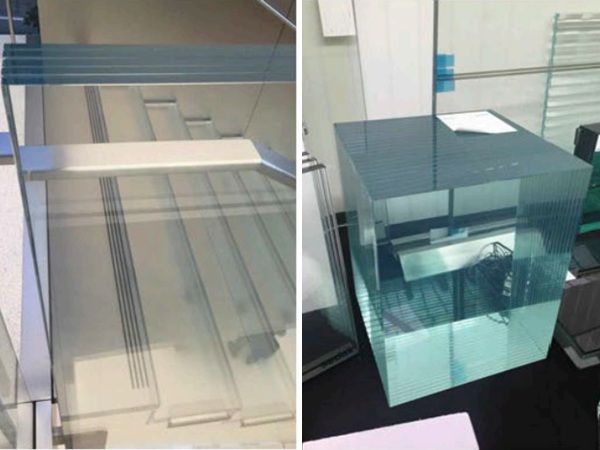
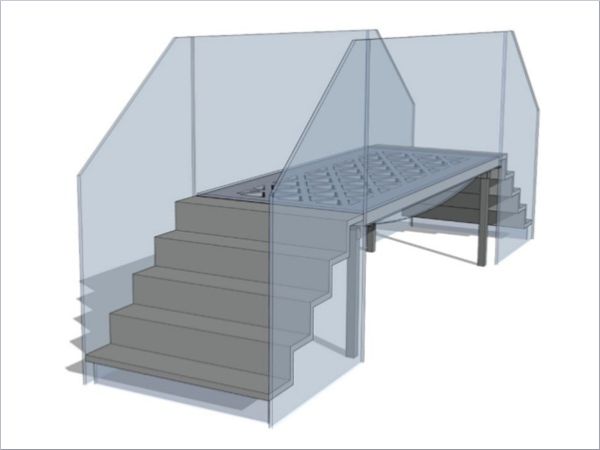
| This article presents how the pioneering G2C (Glass-to-Concrete) project is redefining construction by successfully integrating bonded glass and concrete into a full-scale pedestrian bridge demonstrator.
| Reducing energy consumption in glass tempering is no longer optional — and new cooling innovations are making it achievable.
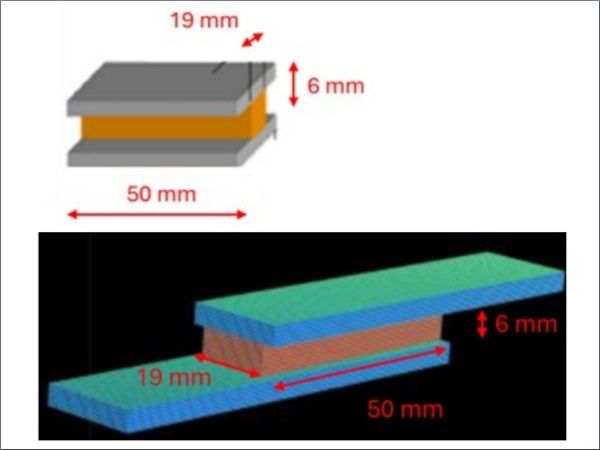
| This study demonstrates how fibre-reinforced and ultra-high-performance concretes enable structurally bonded glass-to-concrete systems, opening new possibilities for efficient, sustainable, and visually striking hybrid structures.
| A new study explores how smarter structural design and adhesive optimization in glass-metal façades can significantly cut embodied carbon while maintaining performance and integrity.
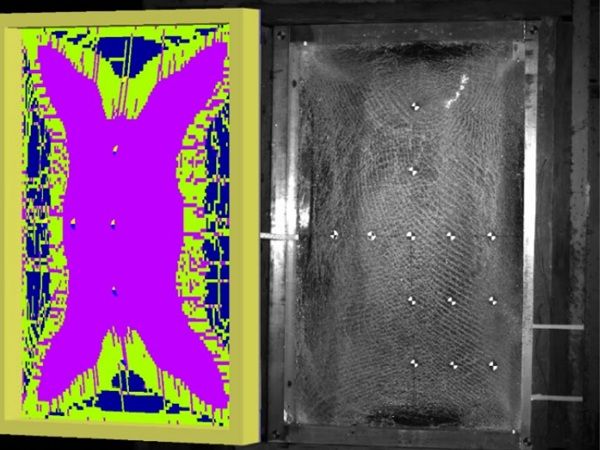
| Understanding how glazing systems behave under blast conditions is essential for designing safer, more resilient façades.
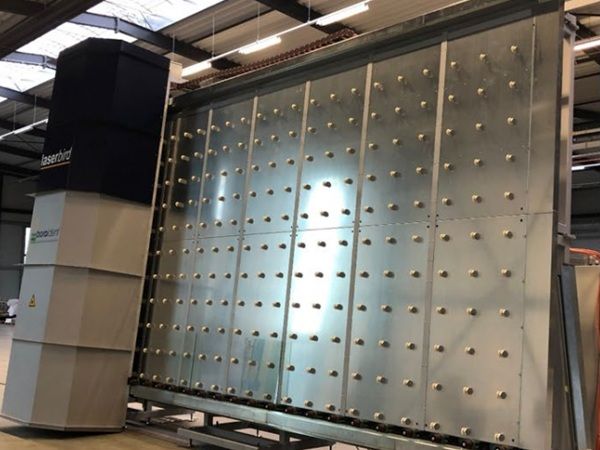
| Laser technology is rapidly reshaping the future of glass processing, offering a level of precision and innovation that traditional methods can’t match.
| As the façade industry advances in sustainable glass coatings, it’s time to look beyond energy performance and focus on human-centered design—exploring how light, spectrum, and transmittance impact our wellbeing.
| Smart glass, simplified. Meet OSSE, Organic Semiconductor Materials for Sustainable Electronics, from the University of Turku.
| A new paper explores the complete process and equipment innovations enabling the handling, cutting, and manufacturing of ultra-thin boro-aluminosilicate glass for architectural applications.
| Advances in architectural design and energy-efficient construction are reshaping expectations for modern glazing solutions.
| At Step Change 2025, ReViSalt demonstrated how its innovations are reshaping the future of glass strengthening.
| Fresh from Step Change 2025, Lithium Designers GmbH, the Frankfurt-based innovators transforming façade planning through parametric design and 3D-printed nodes, shared their insights on how technology is reshaping the future of architectural design.
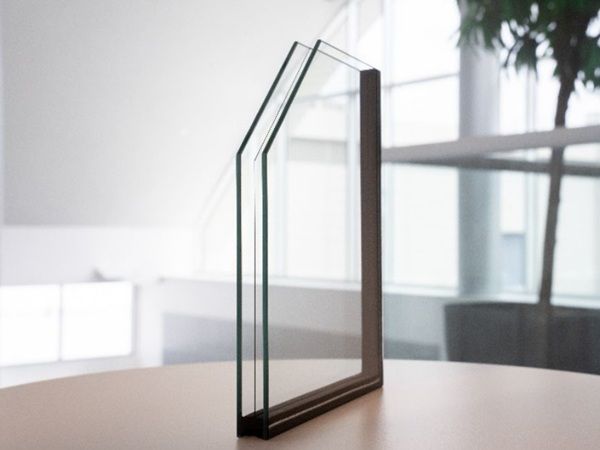
| The path to low-carbon, high-performance facades depends on mastering the long-term thermal behavior and lifecycle performance of Insulating Glass Units (IGUs).
| At Step Change 2025, in connection with Glass Performance Days 2025, eLstar Dynamics wowed us with their smart glass tech that dynamically shifts from ultra-dark (0.1% transparency!) to crystal clear (up to 70%).
| Viprotron has developed a new technology for the exit of the furnace, that allows the measurement of the distortion of tempered glass with high precision and unparalleled repeatability.
| ASTM has introduced a new standard, ASTM E3401, to guide the safe use of laminated glass in swimming pools, aquariums, and other applications subject to hydrostatic loads.
| In this eighth episode, we delve into optimizing energy efficiency in Low-E production.
| New international standards are reshaping the way modern façade glass is designed, balancing security performance with comfort, safety, and multifunctionality.
| Discover how TPS® boosts IGU longevity and energy performance in this Glastory blog and download the presentation.
| The growing use of glass in modern architecture has increased the importance of laminated safety glass (LSG), prompting new research into how production processes impact its long-term durability and safety.
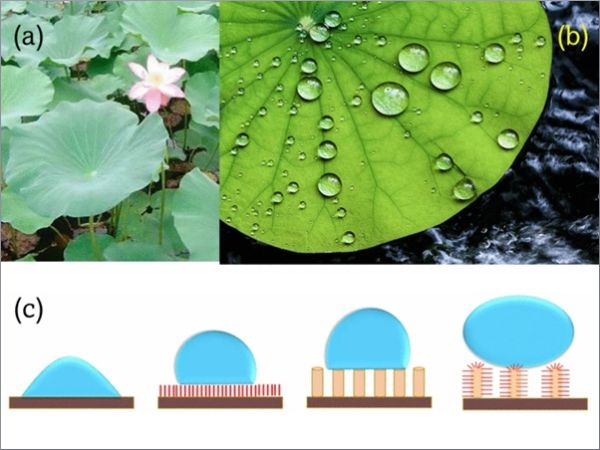
| Self-cleaning surfaces, enabled by advanced material design and additive manufacturing, are opening new possibilities for sustainable and multifunctional technologies.
| Dive into the blog to learn how cutting-edge solutions are making ultra-thin glass production possible—and scalable.
| Mikko Rantala on Glastory: Glass tempering is an energy-hungry process, and not just because of the heat.
| This paper investigates the integration of colorimetric analysis into the architectural glass selection process, with a focus on utilizing spectral data to quantitatively characterize colour attributes.