High strength glass
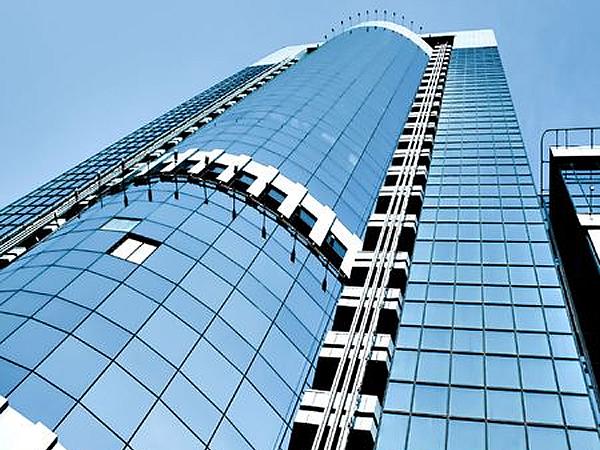
Glass facades are state-of-the-art and highly desirable in many different fields, from big corporations to residential buildings. Such large structures must have the capacity to withstand the pressure they are subjected to during the building process as well as Mother Nature once completed.
Over the past decade, numerous developments have been made in the construction of buildings created with glass, from the bonding process to bent and curved design.
Thus, while glass may seem fragile, it can be an extremely strong and durable material when created properly and in conjunction with the right materials. Overall, its sleek look combined with its robustness makes glass the perfect material for city developments.
The proposed “Big Bend”
One major architectural endeavor using glass has recently been proposed for New York City. The project aims to create a building using bent glass that would result in a 4,000-foot-long skyscraper.
This would far surpass the current longest building in the world: the Burj Khalifa in Dubai, which is both the tallest and longest structure at 2,722 feet.
To achieve this never-before seen length, the architects plan to use a U shape design, which was created by Ioannis Oiaonomou of the Oiio Studio.
The U design would allow the architects to work around the city’s zoning laws regarding building height. Deemed the “Big Bend,” the project is currently seeking an investor to help bring it to life.