Others also read
| Toughened glass: requirements on physical security, climate resilience and cyber security are rising
| As glass increasingly takes on structural roles in modern architecture, ensuring its fire resistance has become a critical challenge for safe building design.
| This study explores how fibre optic sensors can accurately measure strain and temperature in laminated glass systems, revealing how adhesives, temperature, and load conditions influence the mechanical behaviour of PVB and embedded sensors.
| As the façade industry advances in sustainable glass coatings, it’s time to look beyond energy performance and focus on human-centered design—exploring how light, spectrum, and transmittance impact our wellbeing.
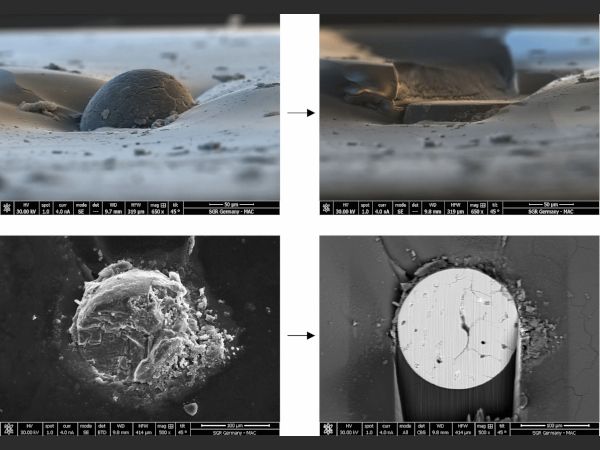
| Spontaneous glass breakage caused by nickel sulfide (NiS) inclusions remains a hidden yet critical challenge in architectural glazing, raising important questions about safety, quality, and prevention in modern glass production.
| Viprotron has developed a new technology for the exit of the furnace, that allows the measurement of the distortion of tempered glass with high precision and unparalleled repeatability.
| ASTM has introduced a new standard, ASTM E3401, to guide the safe use of laminated glass in swimming pools, aquariums, and other applications subject to hydrostatic loads.
| Thermal stress relief treatment offers a promising solution for enabling the reuse and remanufacturing of end-of-life tempered glass, paving the way for more circular economy practices in the flat glass industry.
| New international standards are reshaping the way modern façade glass is designed, balancing security performance with comfort, safety, and multifunctionality.
| New research explores how non-destructive photoelastic methods could improve quality control for large-format thermally toughened glass, reducing reliance on costly and time-consuming destructive testing.
| In this sixth episode of #AskGlaston flat tempering series, we explore how to avoid loading delays in tempering.
| Mikko Rantala on Glastory: Glass tempering is an energy-hungry process, and not just because of the heat.
| Modeling broken laminated glass remains a challenge—this study proposes a simplified numerical approach based on interlayer experiments.
| This paper presents a groundbreaking technological development in the optical quality of tempered glass.
| Spontaneous breakage in tempered glass due to Nickel Sulfide (NiS) inclusions remains a critical topic in the industry—this paper examines the risks, benefits, and effectiveness of heat soaking as a preventive measure across different markets.
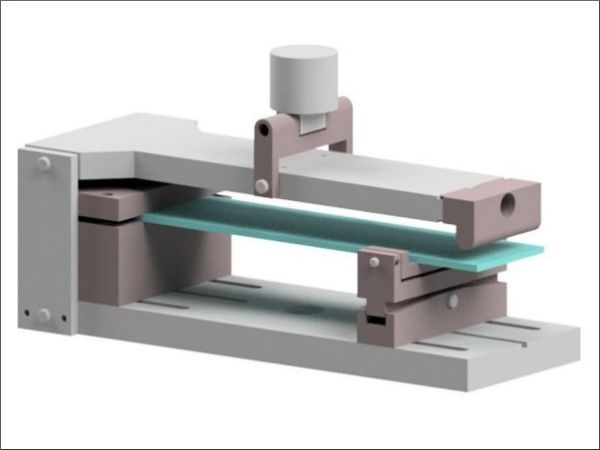
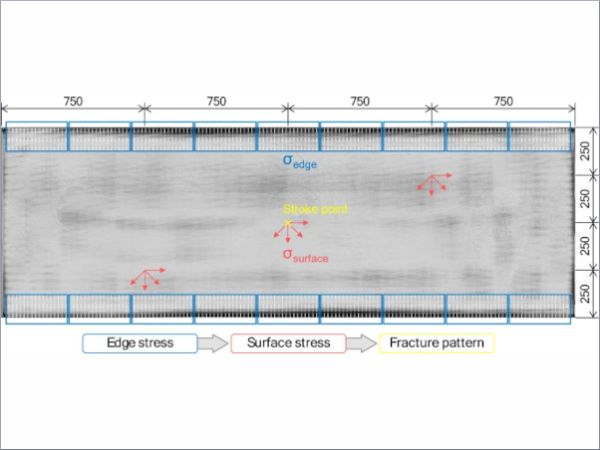
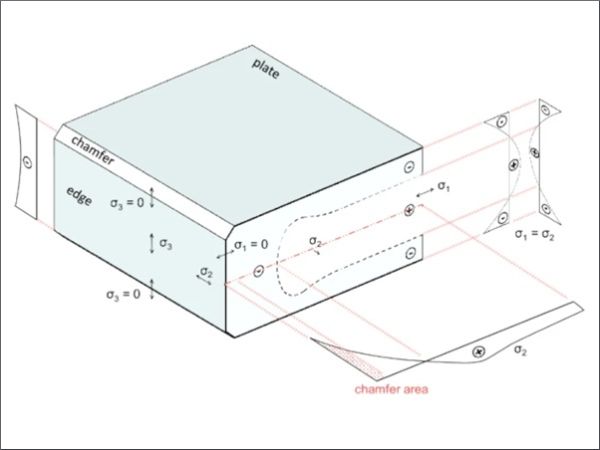
| In this experimental investigation, the surface and edge stress were measured on standardized format thermally toughened safety glass, with different edge processing and glass thicknesses from three different suppliers.
| Can we state if the Heat Soak Test (HST) was done according to EN14179-1:2005 or not?
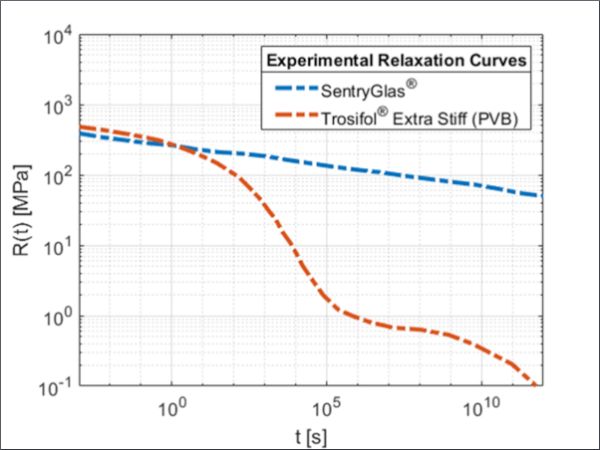
| The aim of this work is the mechanical description of the time-dependent behavior of Polyvinylbutyral (PVB) under large deformations considering quasi-static loading.
| In this paper, two specific liquid cold-poured interlayer adhesives are investigated for their mechanical material properties in an extensive test regime.
| The paper compares fitting functions of different polynomial degrees to determine and assess the edge stress.
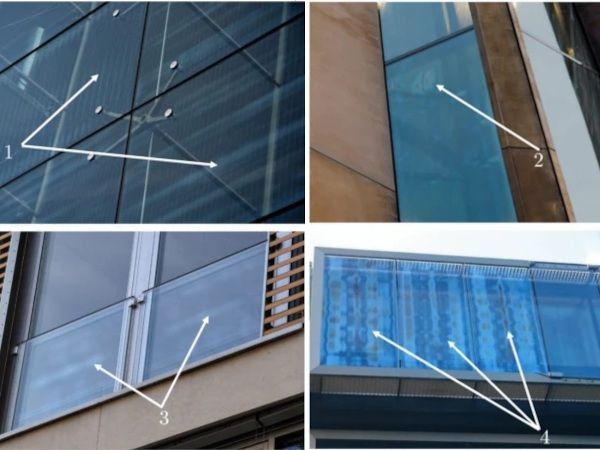
| Minor fluctuations in the tempering process of architectural glass lead to residual stress differences resulting in birefringence and undesired optical iridescence, also known as anisotropy effects.
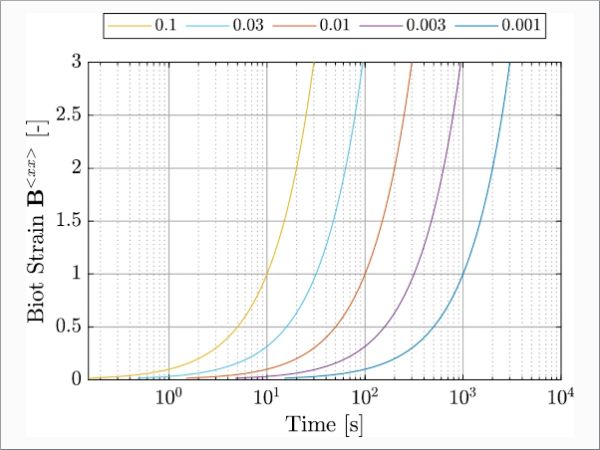
| We discuss a novel approach, based on fractional calculus with a non-uniform time discretization, to numerically simulate interlayer viscoelastic behaviour and associated time-dependent deformation of laminated glass.
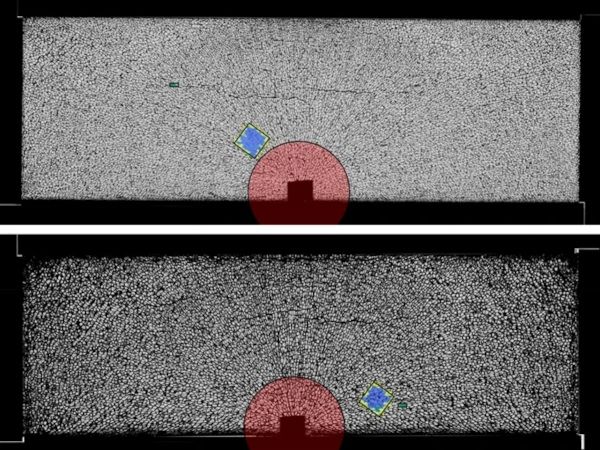
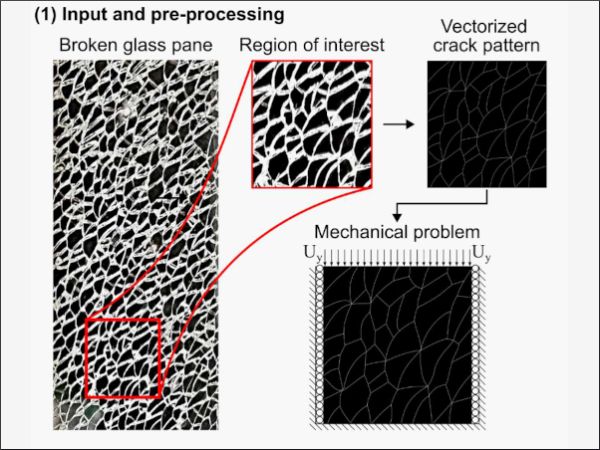
| The objective of the present work is the development and testing of a robust numerical model that can naturally introduce the generated crack pattern into virtual specimens and manage the interaction among many fragments.
| This paper investigates the challenges and potentials of phase-field modelling in simulating glass fracture.