Others also read
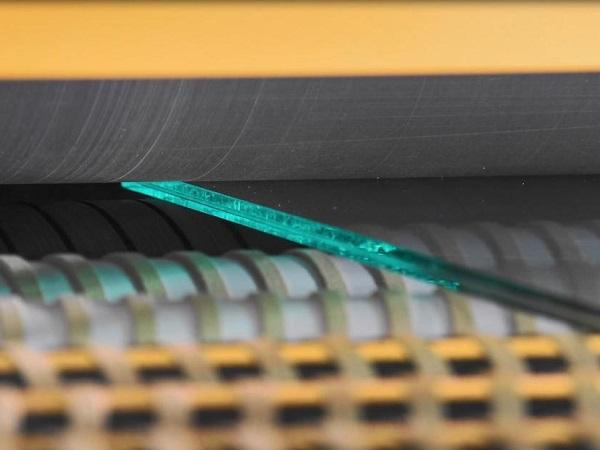
| Gain multiple benefits with upgrades to the glass laminating furnace
| The trend in modern architecture towards a steady optimisation of building envelopes is continuing. Beside its function as a design element, a façade also contributes to the building’s energy balance.
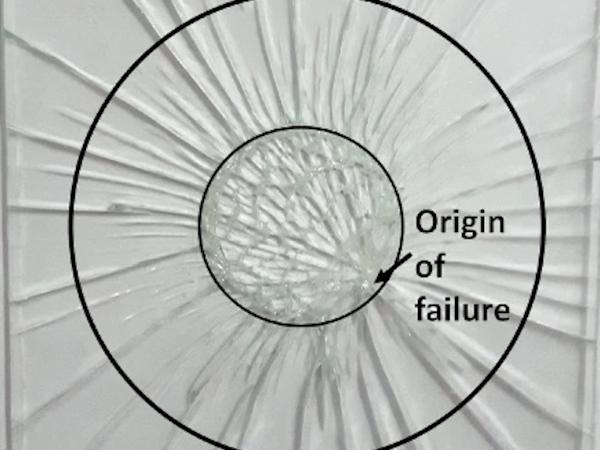
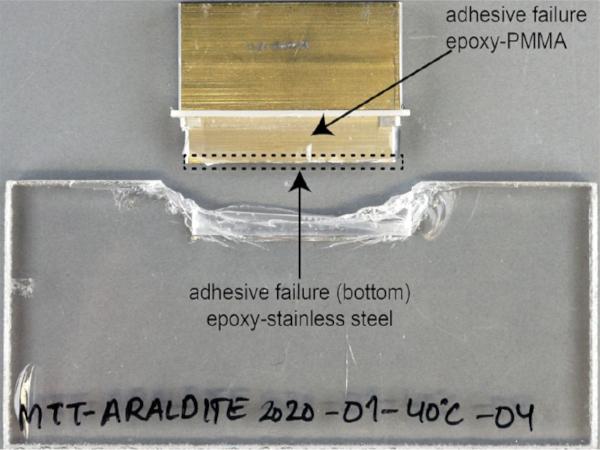
| The durability of an innovative polymeric coating recently developed by the authors to prevent stress corrosion in annealed glass is herein examined.
| An experimental study under tensile loading at +23, +40 and +60 °C and different glass build-ups
| In this third episode of the #AskGlaston flat tempering series, Taneli Ylinen deals with the commonly asked question of how to handle the issues with mixed production.
| In this post, we discuss what emerging designs require and how automotive glass processors can meet these requirements.
| This Glastory blog by Kalle Kaijanen is dealing with the processing of high-strength / structural laminates.
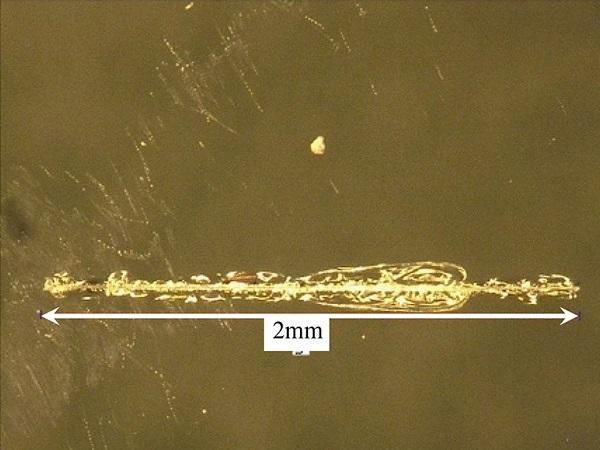
| The strength of glass plays an important role in the dimensioning of glass components in the building industry. A major factor determining float glass strength is damage such as scratches or cracks due to the brittle material behavior of glass.
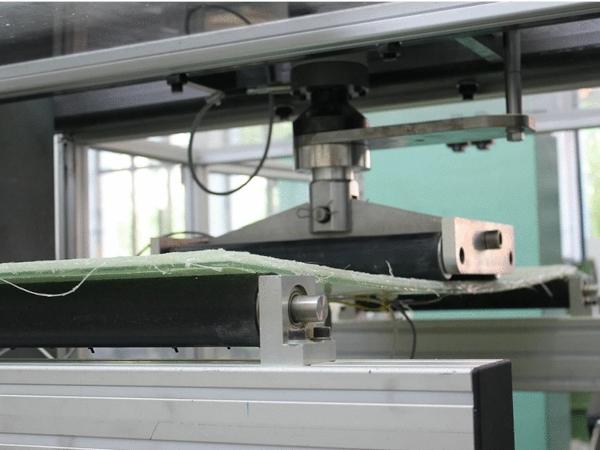
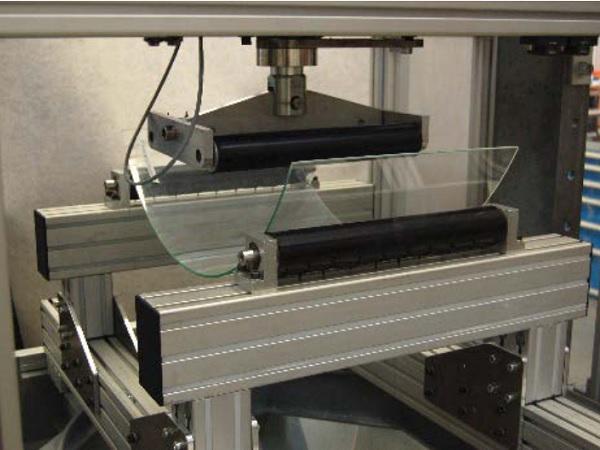
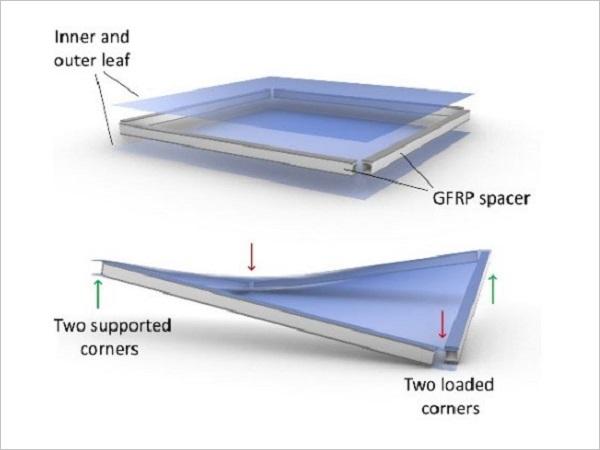
Investigations on the Cold Bending Behaviour of a Double Glazing Unit with a Rigid Edge-Spacer Frame
| In this study, the bending process of specially-fabricated double glazing units (‘panels’) is investigated with a focus on a local instability phenomenon.
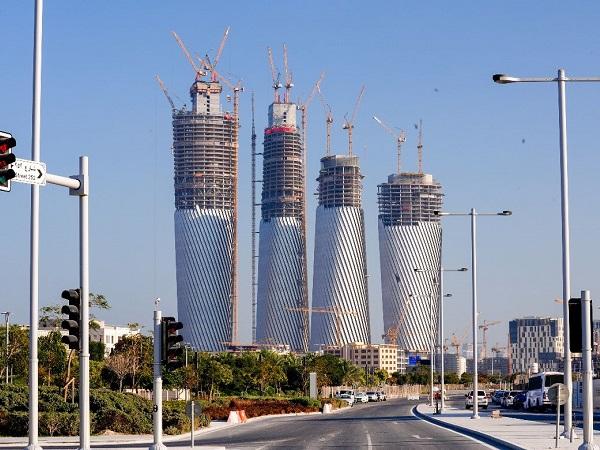
| This paper presents work undergone for a set of four high-rise towers, featuring 11,136 unique cold-bentpanels, hundreds of which are pushed beyond 250mm.
| The paper presents the results of FEM analysis as well as tests performed on double glazed units including Sikasil® IG-25 secondary sealing joints and SikaGlaze® IG-5 PIB as primary seal.
| In the second episode of #AskGlaston Flat Tempering Series, we will talk about the new solution to estimate the stress level in glass – online.
| This first episode is devoted to the white haze phenomenon – one of the most asked about issues in the history of #AskGlaston.
| This latest Glastory blog by Miika Äppelqvist is dealing with the areas of the tempering process that can be improved to make operations more efficient.
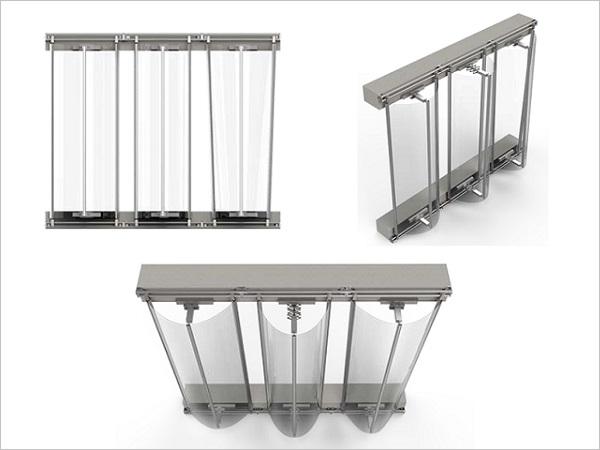
| Thin glass offers the possibility for lightweight and flexible glass façades that could change shape depending on external conditions.
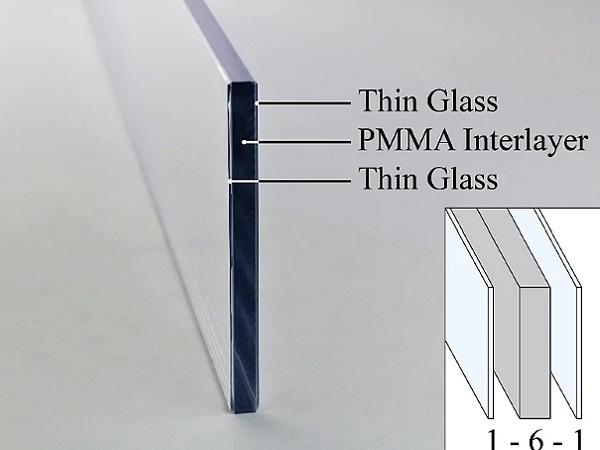
| Novel innovative glass–plastic-composite panels combining a lightweight polymer polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) interlayer core and cover layers of thin glass are currently under development.
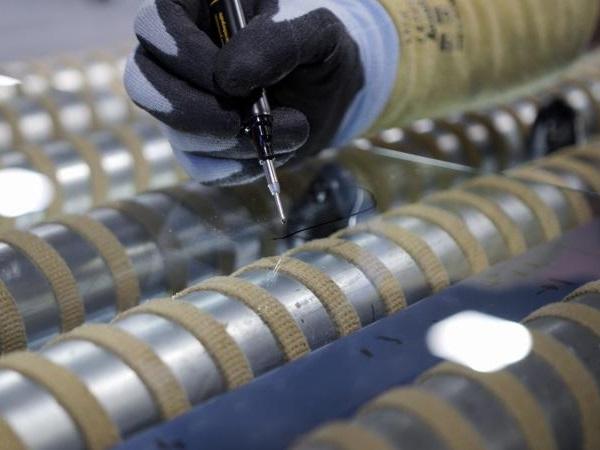
| Industry demand for impeccable glass quality has increased notably over the last years. Customer expectations run high, forcing glass processors to strive for ever-stricter quality control and ensure minimal rejection rates for finished products.
| The most common quality issues that arise in tempered glass are roller waves, glass distortion, bad anisotropy and white haze. In this post, we want to focus on white haze and ways to control it.
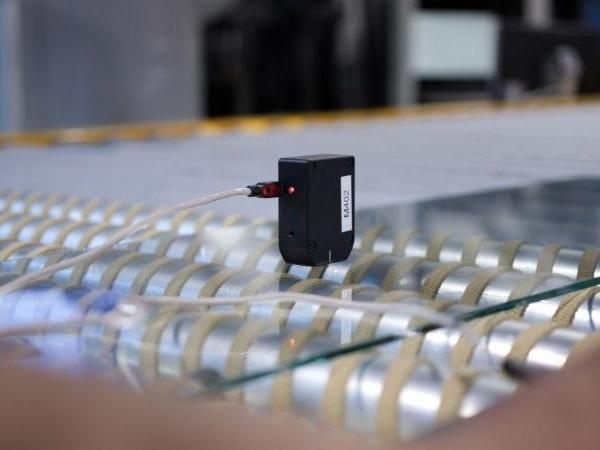
| The use of new generation thin, lightweight and damage-resistant glass, originally conceived for electronic displays, is moving its first steps in the built environment, in particular for adaptive and movable skins and façades.
| Research has shown that the general approach to determine the bending strength of thermally curved glass with the aid of the four-point bending test for flat glass according to EN 1288-3 is applicable.
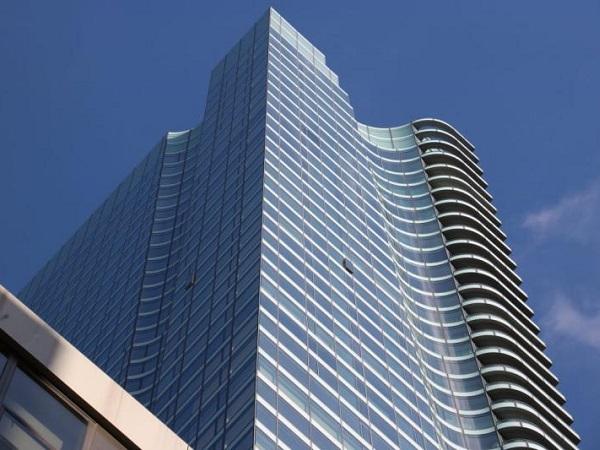
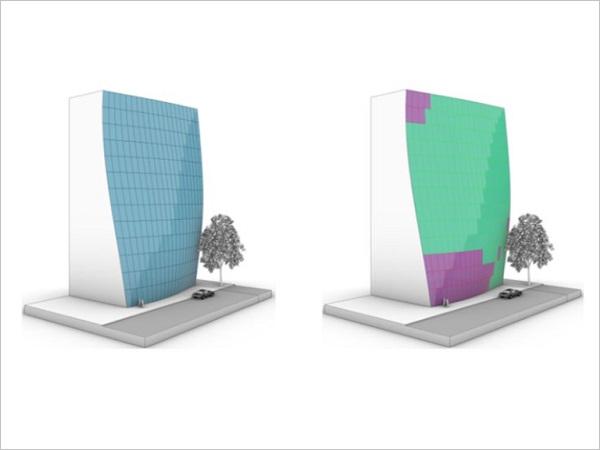
| In 2015, the bold concept of a curvy tower at 252 East 57th Street, New York, was presented to an audience at the Glass Performance Days conference. At that time, building construction was just beginning, and no one was certain such a novel idea could be realized.
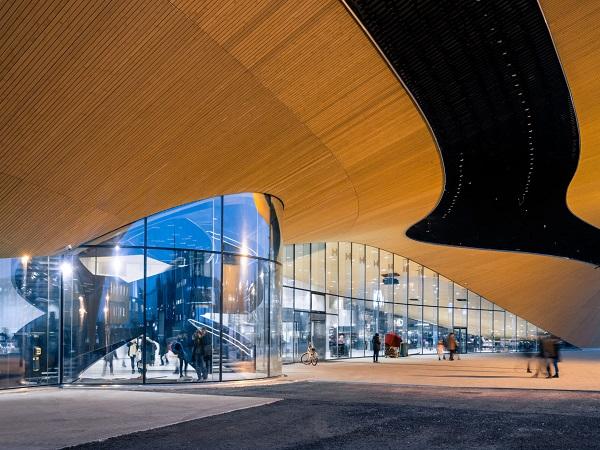
| This poetry in architecture, one of the most advanced structures in the Nordic countries, Oodi Library exalts the very elements of glass, wood and steel that work in balance as a free-standing masterpiece.
| In glass tempering, we look for equipment that uses less energy, leading to fewer emissions. But sometimes, the numbers are too good to be true.
| Global environmental concern is motivating efforts to improve energy efficiency in all industrial sectors. And glass tempering is no exception.
| Today, almost all new devices – from home appliances to production equipment – are connected. Rapid development in consumer electronics has been increasingly moving towards industrial use. In the glass industry, this development is still in its early stages.