Author: Matthias Loppacher | Glaston
Source: glastory.net
As the automotive industry evolves, so do the requirements for automotive glass processing. New vehicle designs call for new and more complex glazing solutions. To meet these demands, manufacturers face a range of processing challenges. In this article, we explore the evolving landscape of automotive glazing and display processing – and discuss strategies for keeping up with the changes.
Adapting to new functionalities and trends
Automotive glass processing is undergoing tremendous changes right now.
To support advanced vehicle designs, exterior glazing must keep up with emerging trends. This includes the integration of head-up displays, heat and solar control coatings, switchable films, camera windows and more. Moreover, the popularity of sunroofs is on the rise as a result of new functionalities.
In the interior, displays are crucial to conveying information, entertaining and personalizing the vehicle experience. Now these displays are getting larger, smarter and often feature special shapes.
At the same time, automotive manufacturers are asking for new glass types, like alumina-silicate or boro-silicate glass, thinner and more lightweight units, better edge quality, higher shape precision, less distortion and new interlayers.
The increasing complexity of exterior and interior glazing poses significant challenges for manufacturing processes and machinery. New processing strategies are being developed to achieve the required precision, minimize waste and enhance overall quality.
Preprocessing is key
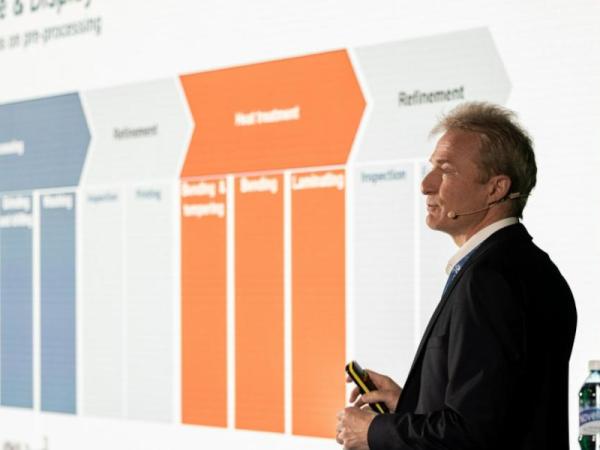
Glass processors must adapt their technologies and processes to keep up with the dynamic industry landscape. One way to ensure conformity to challenging specifications is by leveraging preprocessing capabilities.
First, tighter control over individual process steps, such as cutting, breaking and grinding, is crucial to achieving the best overall result.
The use of artificial intelligence (AI) facilitates real-time quality control after each manufacturing step. AI algorithms analyze data, identify defects or deviations and make adjustments to optimize production outcomes. AI helps minimize waste, enhance overall quality and accelerate production rates.
Second, the preprocessing equipment itself must be updated with new technological solutions developed to provide even better preprocessing results.
The presentation below focuses on preprocessing strategies. It provides an overview of state-of-the-art manufacturing technologies already available for producing the automotive glass of today and tomorrow.


















Comments
AI enables real-time quality control after each manufacturing step by analyzing data, identifying defects, and optimizing production outcomes. This reduces waste, improves quality, and accelerates production rates.