Others also read
| Renovating energy-inefficient buildings is vital to meeting the EU’s climate goals, and new research from Slovakia highlights how material choices can make or break a project’s environmental impact.
| Demand for laminated safety glass is holding strong, driven by rising safety needs and new advances in sustainability and recycling.
| Fused recycled glass proves its strength: recent testing confirms its durability and suitability for architectural use in even the most demanding environments.
| This paper presents experimental and theoretical studies of heat transfer through single- and double-glazed windows with electrical heating of the internal surfaces.
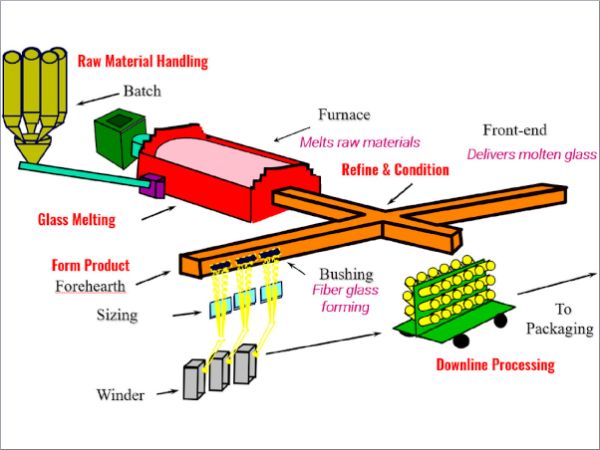
| There are ways to reduce the energy consumption and emissions of glass melting, such as recycling glass, using oxy-fuel burners, improving furnace insulation and design, and adopting electric melting technologies.
Artificial Intelligence Impacts on Architecture and Smart Built Environments: A Comprehensive Review
| This study explores the transformative role of artificial intelligence (AI) in designing and managing sustainable urban environments.
| The main objective of this paper is to explore the effects of ageing and exposure to indoor and outdoor environment on the strength of glass.
| A recent study by BV Glas and Stuttgart University outlines three pathways to achieve climate neutrality in the glass industry by 2045.
| This paper aims to quantify the savings achieved through the ERM of secondary layer addition to existing glazed facades, for a high WWR office building in cooling and heating dominated climate locations.
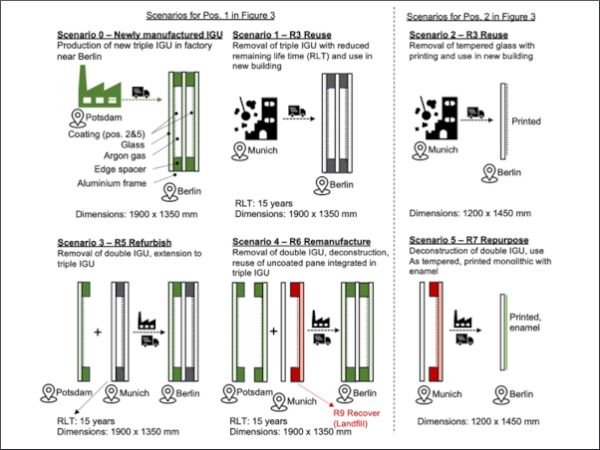
| This paper deals with the question of how old insulating glass units can be re manufactured to match the state of the art in terms of the energy efficiency.
| The thesis examined the barriers to recovering end of life glass from commercial projects in London, and identified the drivers that will open pathways for glass to be recycled.
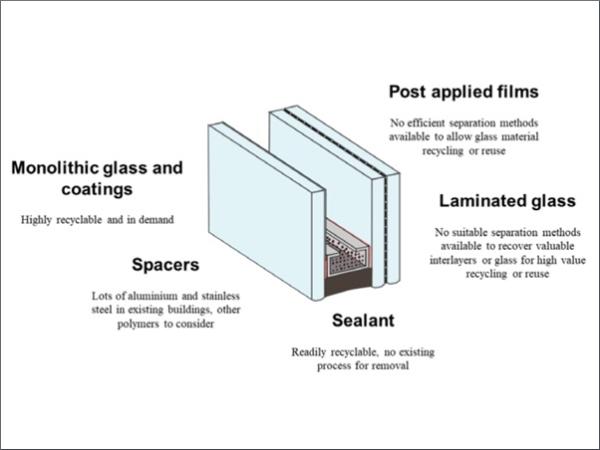
| Increasing the circularity of flat glass does not only mean to collect glass cullet from internal and pre- consumer processes. It also means to use glass cullet from the post- consumer applications, such as residential or commercial buildings.
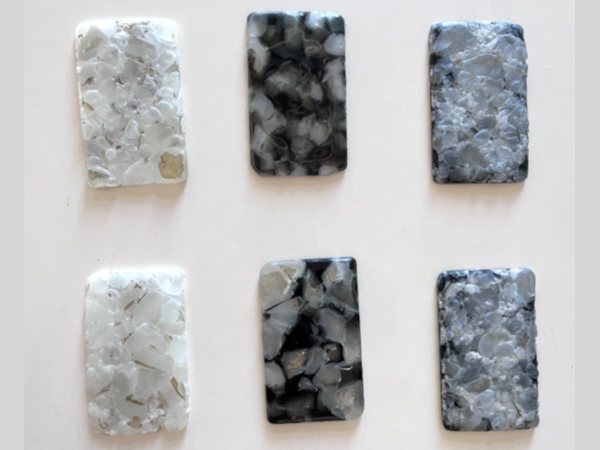
| This research examines the viability of recycling soda lime glass from post-consumer Insulated Glass Units (IGU), mixing various types of architectural glass cullet and fusing them into flat plates by using electric kilns.
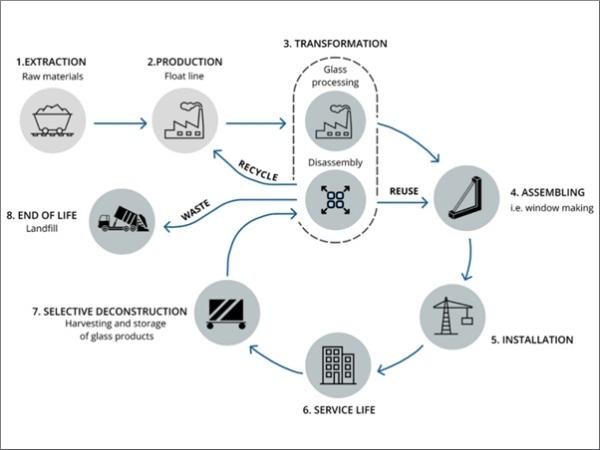
| In order to minimize the environmental impact of glass by preserving the embodied carbon and substituting newly produced glasses, the reuse of glass is considered to be of the highest potential.
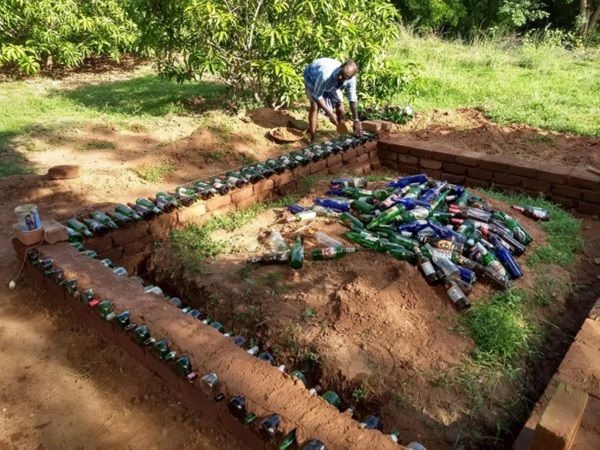
| This research focuses on the incorporation of glass bottles into earth-based constructions, because of their mutual advantages of environmental sustainability and cost-effectiveness.
| ‘glass technology live’ will showcase a promising new development along with many other innovations.
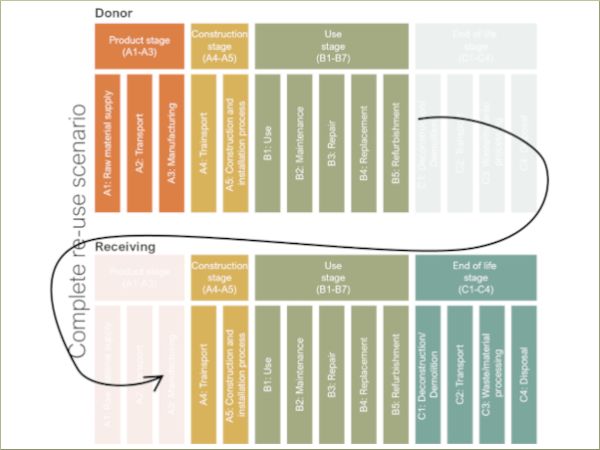
| This article presents the metric avoided carbon for the reuse of aluminium unitised curtain wall façades, that are to be taken from a donor building and applied onto a receiving building.
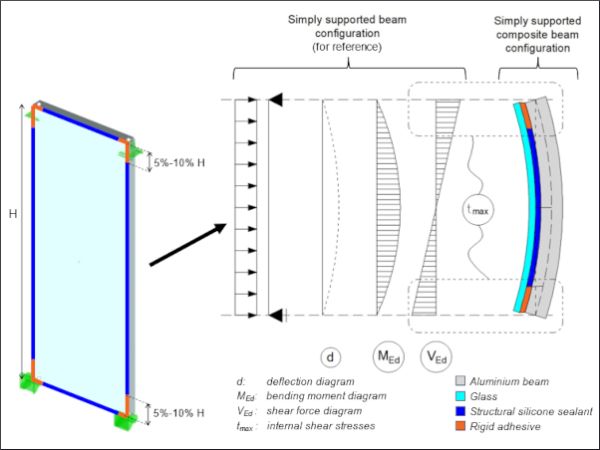
| A Composite Approach in the Design of Glass-Aluminium Facades to Minimise Embodied Carbon Emissions
| The Feasibility of Recycled Glass as a Building Material With Additive Manufacturing
| The approaches proposed by planners and architects for adapting to climate change will be discussed at glasstec 2024 (22-25 October, Düsseldorf) at its Architecture Forum.
| A study of its environmental benefits, quality, and mechanical properties
| Flat glass manufacturers are rightly focused on reducing their operational carbon and in turn the embodied carbon of the glass materials that they create.
| Sustainable growth requires cost efficiency and continuous optimization of processes. Sometimes, it even requires a disruptive change within an organization.
| This paper will review the impact of silicones at various levels of a sustainable design.