Date: 9 October 2001
The award is sponsored by R&D Magazine and honors the year’s 100 most technologically significant new products.
Schott subsidiary Schott Glass Technologies in Duryea, Pennsylvania received the honor for its development of a continuous melting process for neodymium doped phosphate laser glass used in large solid state high-energy laser systems. The manufacturing process speeds up the production rate by a factor of 20 while reducing the cost, benefiting the current construction of the world’s largest lasers in the United States and France.
Schott supplies laser glass to both the National Ignition Facility (NIF) at the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory in California and to the Laser Megajoule (LMJ) project located near Bordeaux for inertial confinement fusion research. The laser glass will enable scientists to achieve the huge energy levels (500 trillion Watt – 5 x 1014 W) required for nuclear fusion research.
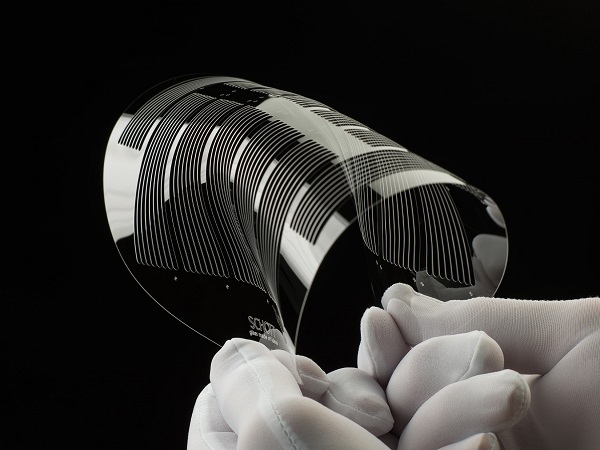
The enormous energy places high requirements on the glass. It is not only required in large volumes, but it also must be highly pure and free from defects such as solid inclusions to prevent breakage caused by the high energy levels achieved in the lasers. Schott devised a continuous, self-containing melting process that accomplished this goal.
The glass is a key component for the NIF laser, which consists of 192 separate laser beams that are brought to a common focus at the center of a fusion test chamber. The NIF laser amplifiers require glass plates measuring 44 x 78 cm and 4.5 cm thick. 16 plates are required for each of the 192 laser sources. At LMJ, 240 laser-beams provide the energy necessary for nuclear fusion. In total Schott is supplying around 4000 glass plates for both projects.
The French and US facilities are being constructed during the same timeframe. The projects complement one another and are characterized by an intensive exchange of information between the scientists involved.





Add new comment