Others also read
| Windows have always been at the intersection of various technologies and architectural processes that evolved in parallel and often intertwined.
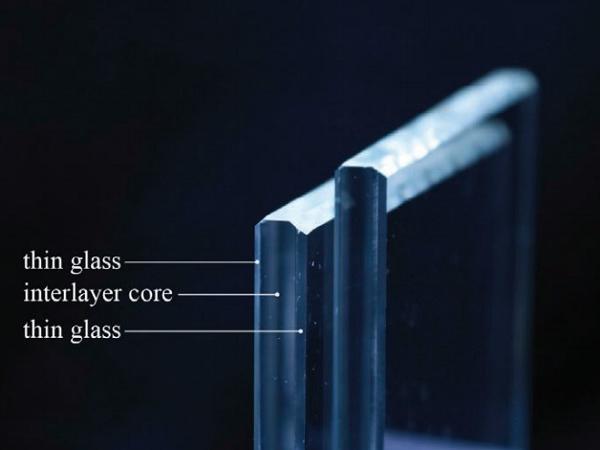
| This contribution is an excerpt of the journal publication by Louter et al. 2018. It explores the potential of thin glass for architectural applications and reports on two thin glass concepts.
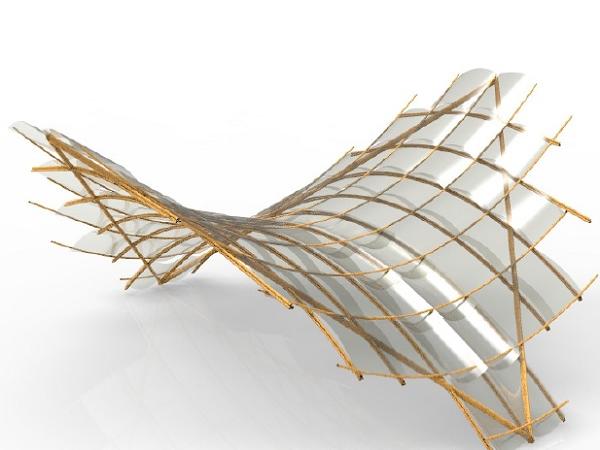
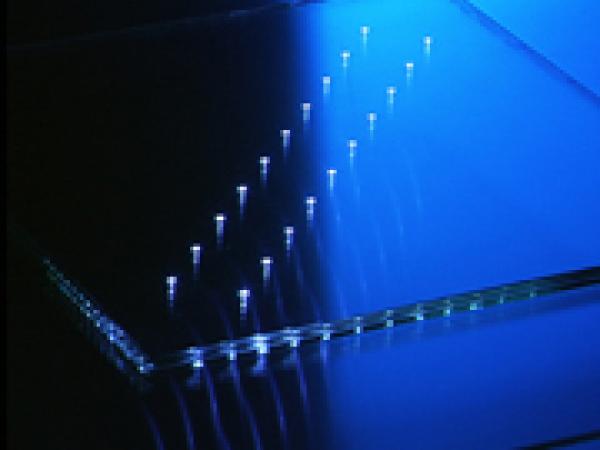
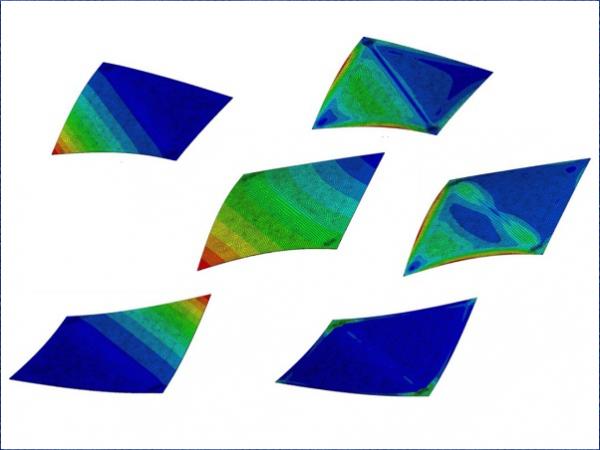
| New generation thin, lightweight and damageresistant glass seems to be the optimal material for extremely deformable structural elements for façades and building skins.
| Researchers and engineers search for solutions to achieve transparent lightweight structures combined with high structural performance.
| Along with the multifunctionality of the building skin, BIPV today involves a new aesthetics in contemporary architecture.
| At glasstec 2018 in Düsseldorf exhibitors will present intriguing developments in the display glass segment. This theme is also addressed in a very special way by the expert conference “Function meets Glass” on 22 and 23 October.
Glass off the roll - Thin glass is revolutionising the performance spectrum of glass and glass panes
| Thin glass – as thin as a razor blade or a human hair – is a reliable method to protect smartphone touchscreens, sensitive filters and sensors.
| To obtain free form geometry for the roof structure, bamboo canes are pre-bent. Thin glass is also cold bent and cladded. The tolerances that occur in bamboo construction are accounted by this flexibility of thin glass.
| Touchscreen displays, LED technology and ultra-thin glasses: The multifunctional diversity of glass in IT and architecture will, in the long term, lead to a combination of both.
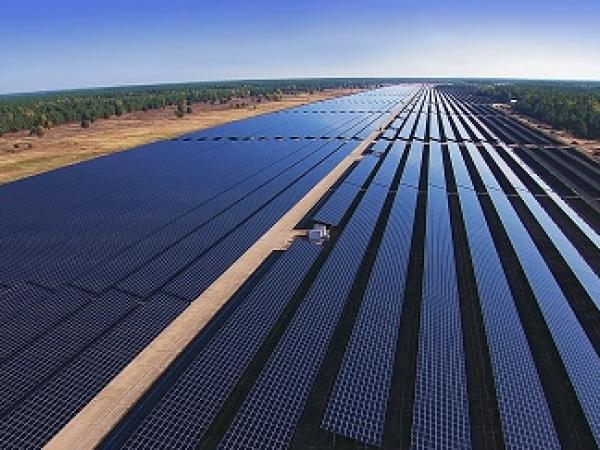
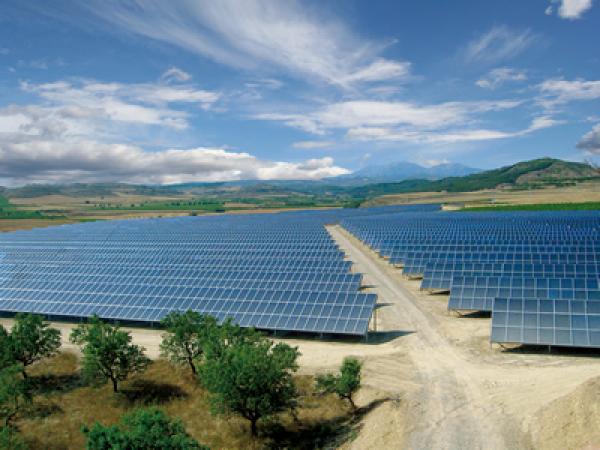
| Cities are eating up an increasing amount of heat and electricity. In order to reduce this consumption, buildings have to become increasingly efficient and integrate more renewable energies.
| The crisis of the photovoltaic industry is drawing to a close. While it is true demand for solar modules is dropping in Europe, demand in many other regions is rising rapidly.
| Although the costs for solar power have come down considerably lately, photovoltaics are still unable to compete with conventional energy sources.
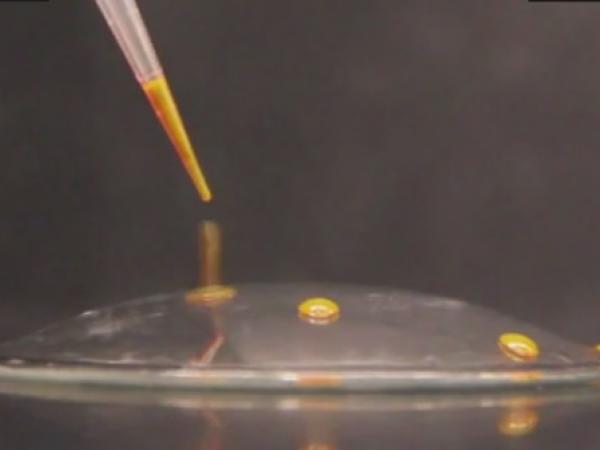
| Resilient, ultraslippery glass could lead to self-cleaning, scratch-resistant windows, lenses, and solar panels
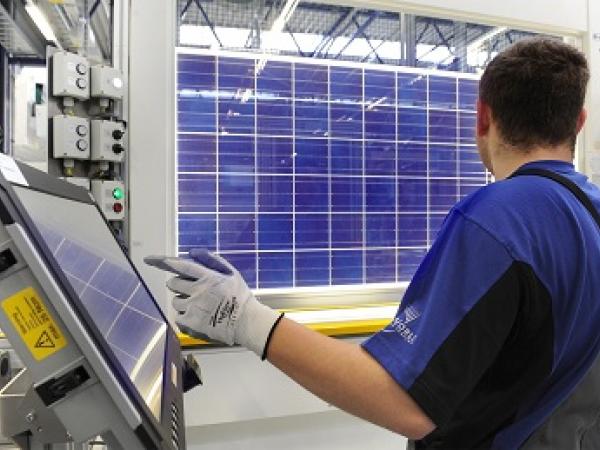
| The following approach describes a new encapsulation technology for glass-glass-modules using tempered thin glass as front and back sheets.
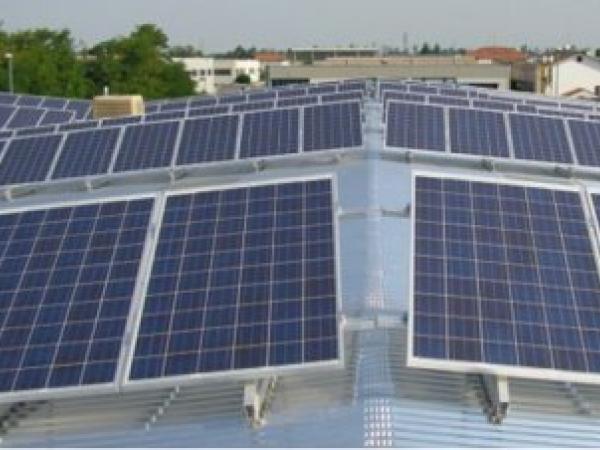
| Photovoltaic modules are components used for the production of electricity from solar energy and, thanks to their morphological and constructive configuration, are suitable for integration in the external skins of buildings.
| PVB is increasingly assuming the leading role among alternative encapsulation materials for solar cells as the alternatives to Ethylene-Vinyl-Acetate (EVA)
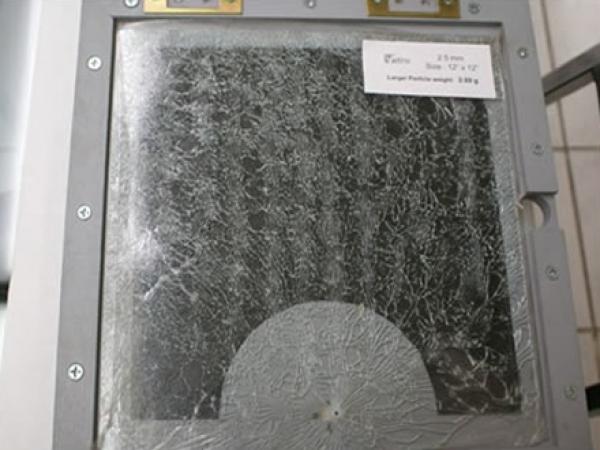
| Advantages of the use of Radio Wave energy in the forming of glass and of tempering thin glass of less than 3.00mm. Some of the inherent problems in the conventional thermal tempering of thin glass are also presented.
| Glass is a versatile material. Especially large area applications such as facade solutions impart their own visual effect and therefore require a targeted selection of the appropriate product.
| The use of transparent glass in conducting electricity using LEDs, short for light emitting diodes, is increasing. LED's are approaching the lifespan of standard building materials, making it cost effective to embed them directly in structural components and architectural finishes.