Others also read
| Glass is reflective in large angles of incidence. Using this property for the detection of shapes is the basic goal of the research.
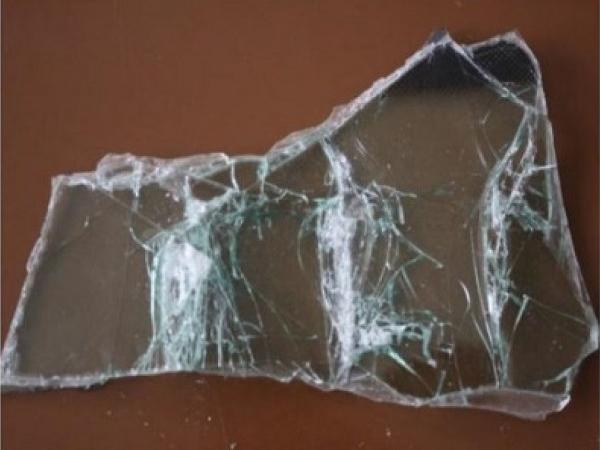
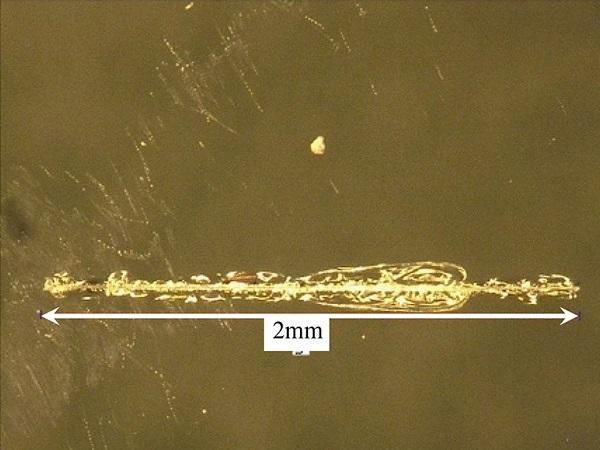
| The paper deals with the recycling of laminated glass, especially with the effective separation of glass (in the form of cullet) from the polyvinyl butyral (PVB) interlayer film.
| End-of-life insulating glass units (IGUs) continue to follow a linear, wasteful path from renovation and demolition sites into landfills or low-value recycling.
| In the present work, subcritical crack growth in soda–lime silicate glass is investigated under different environmental conditions.
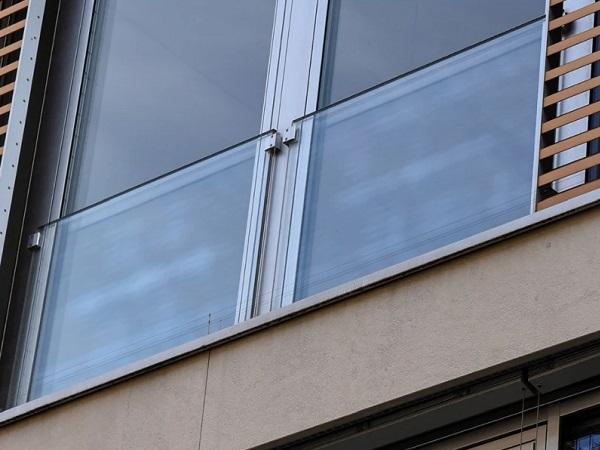
| Glass units are in demand in structural applications, however, the strength is challenging to predict.
| The current study aims to determine the probabilistic fracture strength of glass plates exposed to arbitrary loading and loading rates by a proposed rate-dependent strength prediction model (SPM).
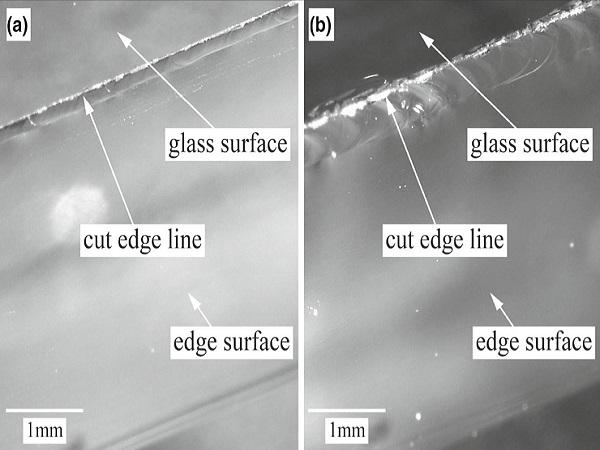
| The article presents some basics about the processing steps of glass edges surfaces, introduces the considered grinding and polishing cup wheels and gives an overview of the performed experimental examinations.
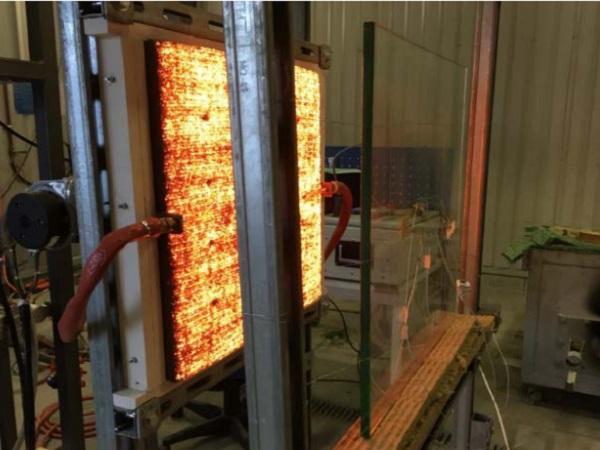
| The paper presents testing of glass panels, static test and dynamic test by hard body impact.
| This document provides an overview of the causes of sunburst delamination in laminated glass.
| The study describes the results of the shear modulus of viscoelastic interlayers made of polyvinyl butyral and provides the basis to define and evaluate a model for the finite element analysis.
| In this third episode of the #AskGlaston flat tempering series, Taneli Ylinen deals with the commonly asked question of how to handle the issues with mixed production.
| The paper is focused on experimental testing of glass-to-glass connection using transparent adhesives.
| Within this research, two sets of real-scale laminated banister panels with the embedded connection were tested.
| An Interlayer Material Study Towards Circular, Dry-Assembly, Interlocking Cast Glass Block Structures
| The results of the classification of hail resistance classes for different materials for greenhouse enclosures are presented in this paper.
| Color Depth is a material-based research project investigating the optical and structural properties of thick glass.
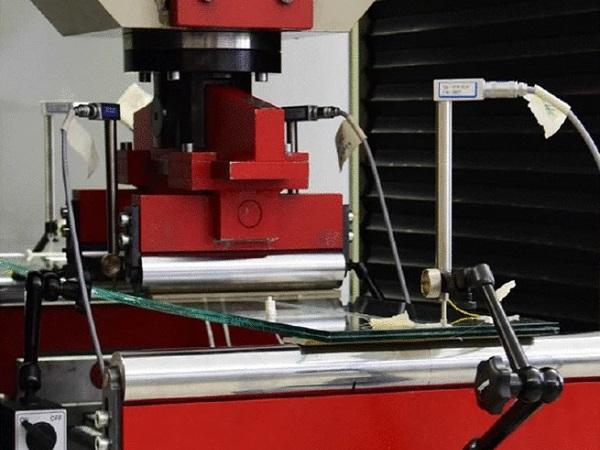
| The strength of glass plays an important role in the dimensioning of glass components in the building industry. A major factor determining float glass strength is damage such as scratches or cracks due to the brittle material behavior of glass.
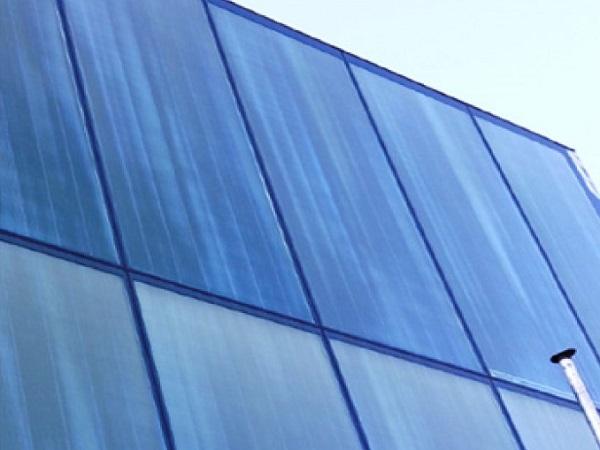
| The main challenge in the design of the duplex façade was the high aesthetical performance that the façade had to meet.
| In this paper, we present the development of an intrinsic parameter σQM characterizing the sensitivity of a coating (or configuration) to the quench marks.
| This first episode is devoted to the white haze phenomenon – one of the most asked about issues in the history of #AskGlaston.
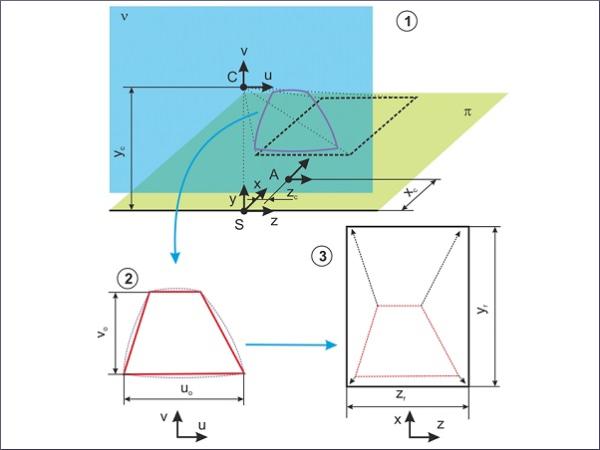
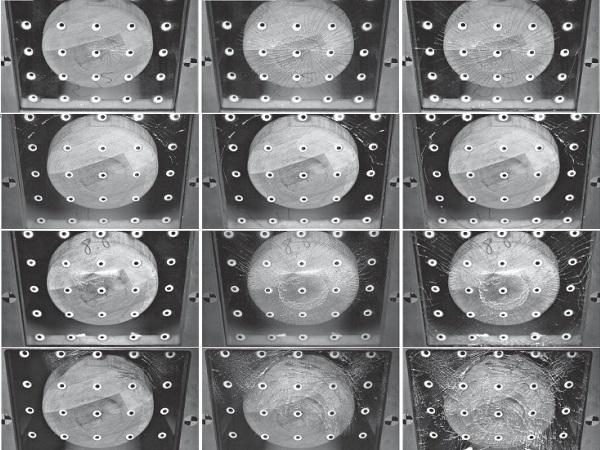
| In the present paper, optical anisotropy effects in architectural glass are evaluated using digital image processing.
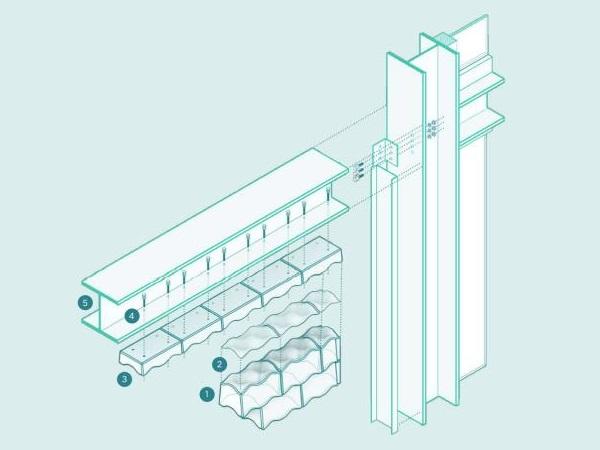
| This paper focuses on a recently developed concept, in which glass is combined with timber to provide post-breakage strength and ductility.
| In this paper, artificial intelligence (AI) will be applied for the first time in the context of glass processing.
| The use of new generation thin, lightweight and damage-resistant glass, originally conceived for electronic displays, is moving its first steps in the built environment, in particular for adaptive and movable skins and façades.
| After seaming, grinding glass edges is another important work step in glass edge processing. The process is primarily used to remove overbreaks and underbreaks at the edges and to process the glass sheets to size.